22
Free URL Encoder: Online Percent-Encoding for URLs (2025)
Instantly convert any text or string into a URL-safe format. Our free URL encoder uses percent-encoding to handle spaces and special characters (?, &, #). Perfect for developers and API calls.
In the structure of a URL, every character matters. A character like ? starts the query string. An & separates parameters. A # starts a fragment. But what happens when you need to put one of those *special characters* inside your data?
If you try to put a space or an & in a URL parameter, the browser will get confused, and your URL will break. The solution is URL Encoding (also known as "Percent-Encoding").
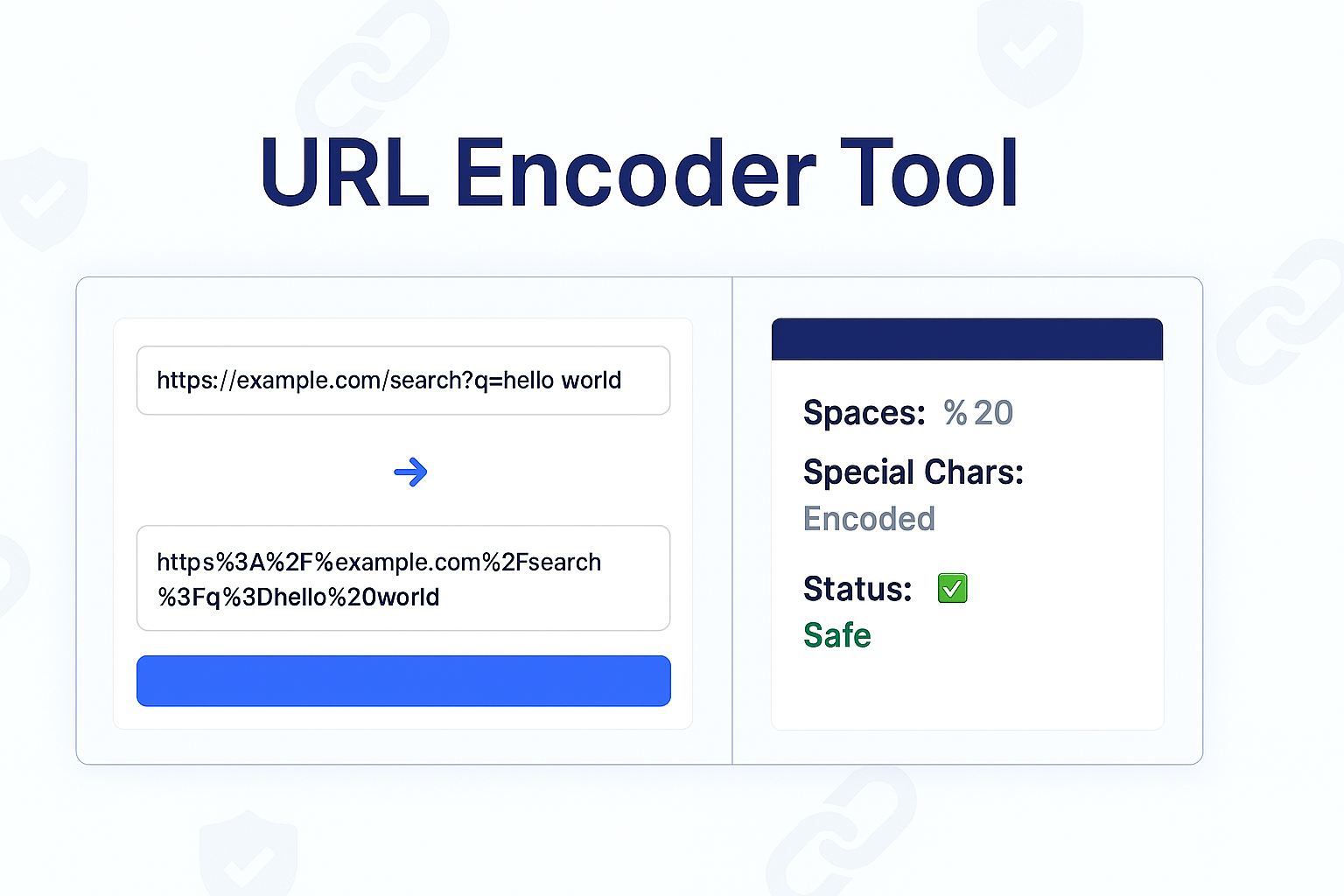
Our free URL Encoder is a simple tool that instantly translates any string of text, including special characters, into a single, URL-safe format that can be safely transmitted over the internet without breaking.
What Is URL Encoding?
URL Encoding is a method for translating special characters into a universally accepted format for use in a URL. It ensures that all browsers and servers can correctly interpret the data.
The process is simple: any "unsafe" or "reserved" character is replaced by a percent sign (%) followed by its two-digit hexadecimal (ASCII) code.
The most common example is the space character. A space is not allowed in a URL. Its ASCII value is 32, which is 20 in hexadecimal. Therefore, a space is encoded as %20.
Example:
If you want to pass this search query: cats & dogs
You must encode it before putting it in a URL. It becomes: cats%20%26%20dogs
Now, the server can safely read the %20 as a space and the %26 as an ampersand, without it breaking the URL's structure.
How to Use Our URL Encoder
- Step 1: Navigate to our free URL Encoder.
- Step 2: Type or paste your text (your URL parameter, search query, or any string) into the input box.
- Step 3: Click the "Encode" button.
- Step 4: The tool will instantly provide the fully encoded, URL-safe string, ready to be copied and pasted.
Who Needs to Encode URLs?
- Web Developers: When building dynamic URLs or passing user-submitted data (like from a search box) into a URL parameter.
- API Developers: Essential for making sure your GET request query strings are formatted correctly and won't fail.
- SEO & Marketers: When manually building URLs with UTM parameters that might contain unsafe characters.
Encoder vs. Decoder
This tool and its companion, the URL Decoder, perform opposite actions:
- URL Encoder (This Tool): Takes human-readable text and makes it machine-safe for a URL. (e.g.,
Hello World→Hello%20World). - URL Decoder: Takes an encoded URL string and makes it human-readable. (e.g.,
Hello%20World→Hello World).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why are only *some* characters encoded?
A: URLs have a set of "unreserved" characters that are always safe: A-Z, a-z, 0-9, and - _ . ~. This tool only encodes the "reserved" or "unsafe" characters (like spaces, /, ?, &, %, etc.) that have special meaning.
Q: Is URL Encoding the same as Base64?
A: No. They are both encoding methods but for different purposes. Base64 is used to represent binary data (like images) as text. URL Encoding is *only* used to make text safe to be part of a URL.
Conclusion
Don't let a stray space or ampersand break your links, forms, or API calls. Use our free URL Encoder to instantly convert any string into a universally safe format. It's an essential tool for any developer's toolkit.
Related Encoding & Text Tools:
- URL Decoder - The opposite of this tool. Decode a URL-safe string back into text.
- Text to Base64 - Convert text into Base64 format for other uses.
- Base64 to Text - Decode Base64 strings back into plain text.
- Text to Slug - Convert your blog titles into SEO-friendly, URL-safe slugs.
Last Updated: October 22, 2025
Contact
Missing something?
Feel free to request missing tools or give some feedback using our contact form.
Contact Us