21
Free Image to Base64 Converter: Embed Images in HTML/CSS (2025)
Instantly convert any image (JPG, PNG, GIF) to a Base64 string with our free online tool. Learn how to embed images directly into your HTML or CSS to reduce HTTP requests and speed up your site.
Every image on your website (your logo, your icons) requires a separate HTTP request for the browser to fetch it. While this is fine for most pictures, these extra server trips can add up and slow down your site, especially for small, critical images.
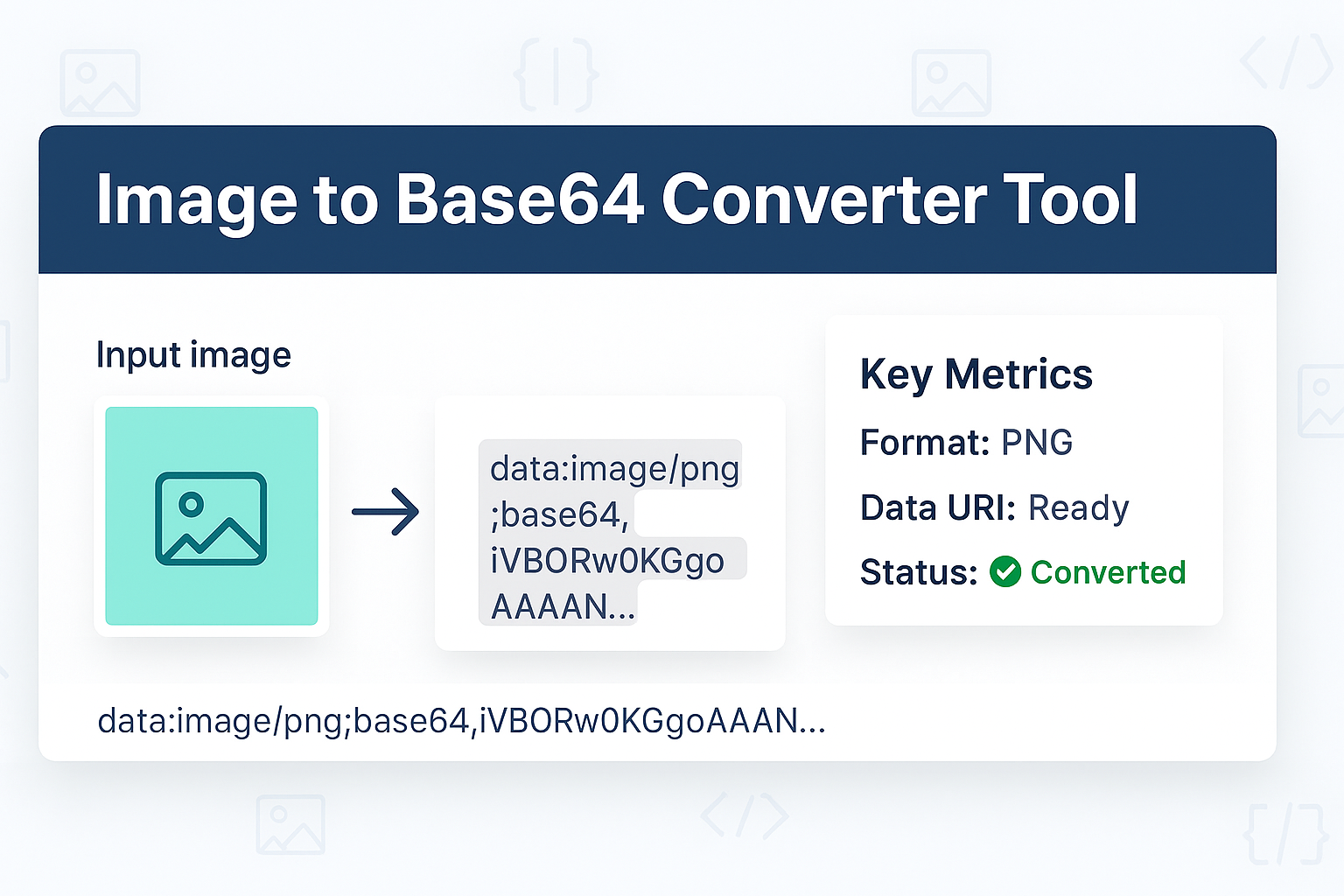
What if you could embed that image *directly* into your code? Base64 encoding makes this possible. It's a method that converts binary data (like an image) into a string of plain text (ASCII). Our free Image to Base64 Converter is the easiest way to do this.
This tool instantly generates the Base64 "Data URI" for your image, allowing you to paste it directly into your HTML <img> tag or your CSS background-image property, eliminating the HTTP request entirely.
How to Use Our Image to Base64 Converter
- Step 1: Navigate to our free Image to Base64 Converter.
- Step 2: Upload your image file (e.g., a
.png,.jpg, or.gif). - Step 3: The tool will instantly convert the image and generate the output.
- Step 4: You can copy the raw Base64 string, the full
<img>tag, or the CSSbackground-imagerule, ready to paste into your code.
Why Embed an Image with Base64? (The Pros vs. Cons)
Using Base64 is a trade-off. It's a fantastic optimization in one situation and a terrible one in another. Here’s the simple rule.
The PRO: Fewer HTTP Requests
This is the only reason to use Base64. For a very small, critical image (like a 2KB loading spinner or a tiny icon), it is *faster* to include it directly in the HTML or CSS. This is because the browser doesn't have to make a separate server request to fetch the image file, so it can render the page sooner.
The CONS: Larger File Size & No Caching
- Larger File Size: A Base64 string is about 33% larger than the original binary image file. This is a *terrible* trade-off for a large photo. A 100KB photo would become ~133KB of text, bloating your HTML or CSS file and making it *slower*.
- No Browser Caching: This is the biggest drawback. A Base64 image is part of your HTML/CSS. If you embed your logo on every page, the user has to re-download that big text string *every single time* they load a new page. A separate image file (like
logo.png) would be downloaded once and then "cached" by the browser for all other pages.
Conclusion: The Best Practice
Here is the rule used by top SEO experts and developers:
You SHOULD use Base64 for: Very small, non-repeating images like tiny icons or a single background pattern.
You should NOT use Base64 for: Large images, photographs, or common, site-wide images like your main logo (which should be cached).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is this tool free to use?
A: Yes! Our image to Base64 converter is 100% free with no limits.
Q: Is my image upload secure?
A: Yes. All conversion is done instantly in your browser. Your images are never sent to or stored on our servers. Your data remains completely private.
Q: What is a "Data URI"?
A: A Data URI is the formatted string that tells the browser what kind of data it is. For example: data:image/png;base64,...(long string).... Our tool generates this for you automatically.
Conclusion
Used correctly, embedding images with Base64 is a clever optimization that can shave precious milliseconds off your page load time. Use our free tool to instantly generate the code you need for your small icons and graphics.
Try Our Free Image to Base64 Tool
Related Encoding & Image Tools:
- Text to Base64 - Convert plain text into Base64 format.
- Base64 to Text - The reverse of our other tools; decode Base64 strings.
- Image Compressor - Make your JPG and PNG files smaller *before* you convert them.
- Image Resizer - Resize your images to the perfect dimensions.
Last Updated: October 21, 2025
Contact
Missing something?
Feel free to request missing tools or give some feedback using our contact form.
Contact Us